Alright, settle in, and let’s talk about something fundamental in the world of cybersecurity: the analysis of malicious software. It’s no exaggeration to say that understanding how the adversary operates is paramount to mounting a proper defense. We’re not just talking about running a file through an antivirus engine; we’re talking about malware analysis, a deep technical investigation into the heart of malicious code. It’s less a simple process and more a craft, one that demands skill, dedication, and the right tools, much like a master craftsman carefully selecting their instruments.
Why bother with this intricate craft? Because malware isn’t just a nuisance; it’s the digital weapon of choice for criminals, nation-states, and other malicious actors. By analysing it, we aim to understand precisely what it does, how it achieves its malicious aims, how it spreads, and potentially even who is behind it. This knowledge is essential for building effective defenses, developing detection strategies, and responding to incidents. The threats are constantly evolving, with old techniques often reappearing in new guises across various platforms.
At its core, malware analysis typically employs two main approaches:
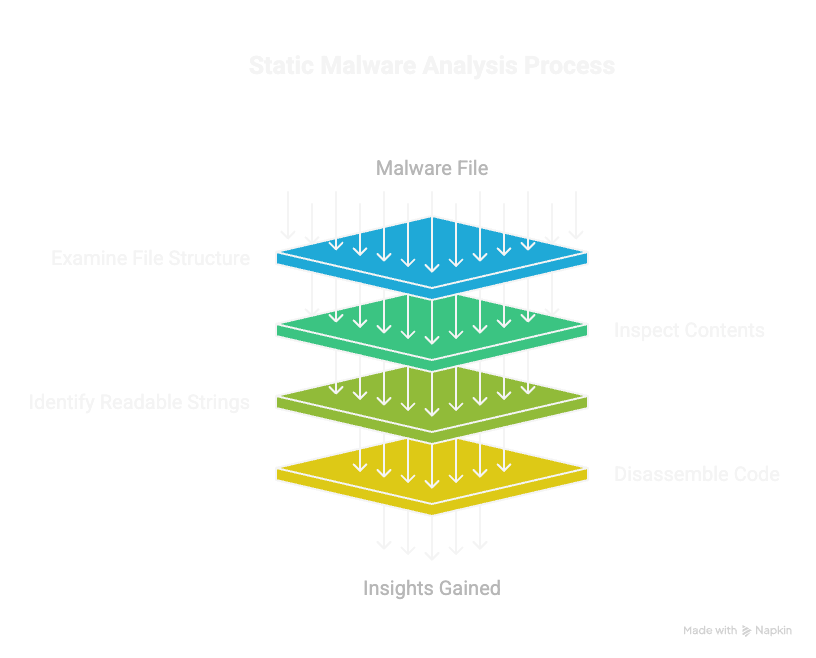
1. Static Analysis: This involves examining the malware without executing it. Think of it as studying the blueprints and materials of a building before construction even begins. You’ll look at the file’s structure, its contents, any readable strings, and its disassembled code to glean insights. It’s a form of reverse engineering.
2. Dynamic Analysis: This involves running the malware in a carefully controlled environment to observe its behaviour. This is necessary because malicious software often tries to hide its true nature until it’s executed. By running it in a sandbox or virtual machine, you can see what files it touches, what network connections it makes, and what processes it interacts with. It’s like observing the building in action after it’s built.

These two approaches aren’t mutually exclusive; a skilled analyst will almost always combine them to get the fullest picture of the malware’s capabilities and intent.
The digital landscape is vast, and malicious logic appears in many forms – viruses, worms, and Trojan horses are just a few common types. This craft is also platform-agnostic; while Windows has historically been a major target, analysis techniques are crucial for understanding threats on macOS, Linux, and other operating systems as well.
To truly excel in this craft, you need more than just a collection of tools. Aye, tools like debuggers and disassemblers and network monitors are essential, but the real skill lies in knowing how to use them effectively, to coax out the secrets hidden within the code. This requires a solid technical foundation, including an understanding of x86/x64 assembly and disassembly, and often programming concepts. It’s a discipline learned through practice and experience, diligently piecing together clues just like any good investigator.
This introduction merely scratches the surface of what malware analysis entails. Over the course of this series, we’ll lift the lid on the technical details of static analysis, delve into the intricacies of reverse engineering, explore dynamic analysis environments, discuss how to identify related threats using data-driven methods, and even touch upon the role of data science in automated detection.
Consider this the sharpening of your sgian-dubh – preparing your essential tools and understanding the basics before we delve deeper into the cuttin’ edge techniques.
What’s Next in the Series? (Planned Topics)
Here’s a glimpse into the technical subjects we plan to cover in future posts in this series, drawing from the wealth of information available:
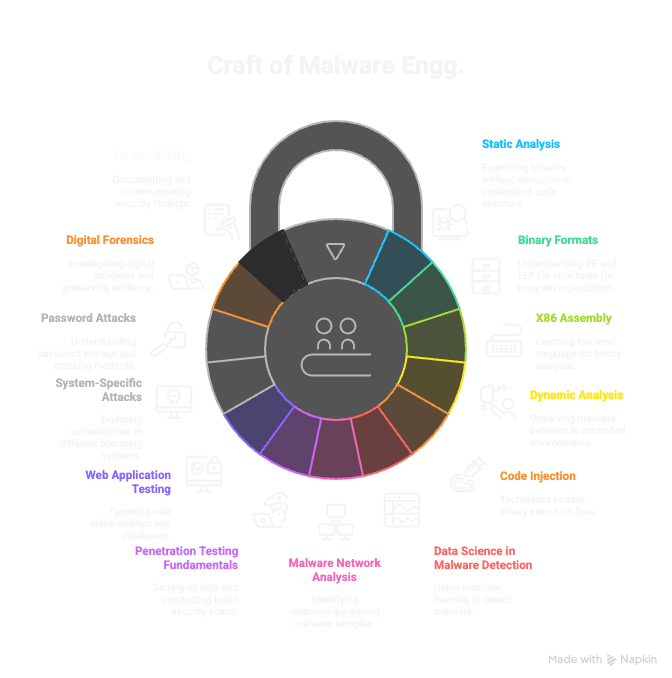
- Static Analysis & Reverse Engineering Fundamentals: We’ll delve deeper into examining binaries without executing them, exploring techniques like disassembly and understanding fundamental concepts needed to analyze code statically.
- Binary Formats: PE and ELF Explained: A detailed look at the structure of Windows Portable Executable (PE) and Linux Executable and Linkable Format (ELF) files, which is crucial for understanding how programs are organized and loaded.
- Introduction to X86 Assembly for Reverse Engineering: Understanding the low-level language that software is translated into is vital for binary analysis. We’ll cover key x86 assembly concepts.
- Deep Dive into Dynamic Analysis Techniques: We’ll explore methods for safely executing malware and observing its runtime behavior, discussing controlled environments and binary instrumentation.
- Code Injection & Binary Modification: Examining techniques attackers use to alter the execution flow or content of existing binaries.
- Applying Data Science to Malware Detection: How machine learning and data science techniques can be applied to build automated detectors and analyze large datasets of malware.
- Malware Network Analysis & Shared Code Detection: Techniques for identifying relationships and patterns among malware samples, such as finding shared code or building malware networks.
- Fundamentals of Penetration Testing: An introduction to setting up your lab environment, conducting reconnaissance (OSINT), and basic scanning techniques used in offensive security.
- Web Application Penetration Testing: Targeting web servers, databases, and common web vulnerabilities using tools and methodologies.
- Attacking Specific Systems: Windows, macOS, and UNIX: Exploring the unique aspects and vulnerabilities when performing security assessments across different operating systems.
- Password Attacks and Cracking Techniques: Understanding how passwords are stored and the methods used to guess or crack them.
- Introduction to Digital Forensics: The process of investigating digital incidents, preserving evidence, and analyzing artifacts from compromised systems.
- Report Writing for Security Professionals: How to effectively document and communicate findings from security assessments, including risk scoring and report structure
Stay Tuned
